The below data was made possible by CMTA, the Charcot-Marie-Tooth Association.
Charcot-Marie Tooth (CMT) disorders are a family of related disorders that produce progressive distal neuropathies, presenting significant challenges for patients and society. CMT1A is the most common form of CMT and is caused by duplication of the peripheral myelin protein 22 gene, resulting in demyelination of peripheral nerves. Psychogenics, in partnership with CMTA, has extensively characterized a mouse and a rat model of CMT1A.
Grip Strength Deficits in CMTA1 Mice and Rats
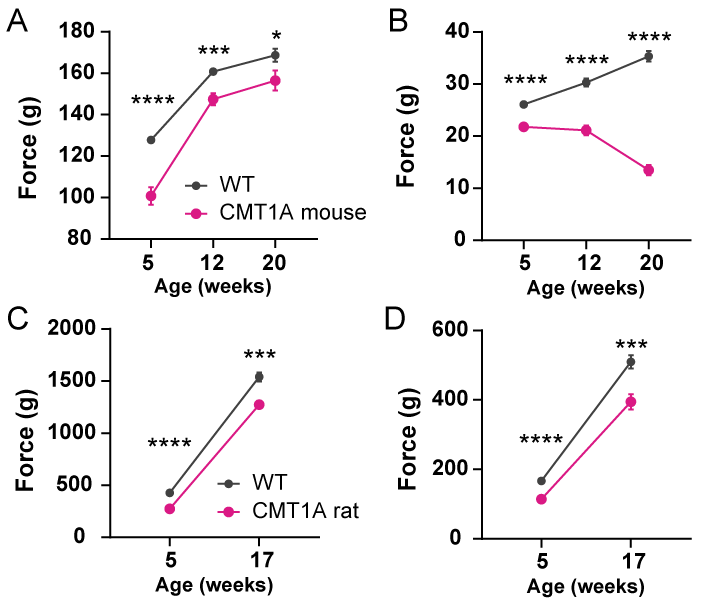
Forelimb and hindlimb Grip strength was significantly decreased in HET mice and rats when compared to their WT counterparts. Deficits were seen at 5, 12, and 20 weeks of age for mice (A, B) and at 5 and 17 weeks of age for rats (C, D).
CMT1A Mice and Rats Show Impaired Performance on The Tapered Beam
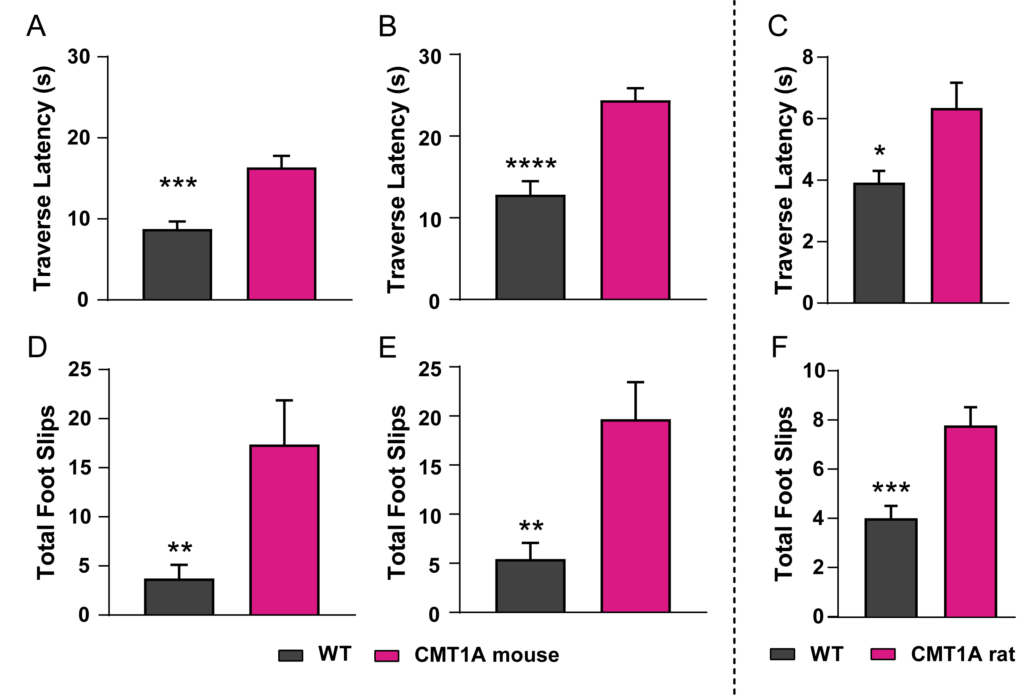
CMT1A mice take longer to traverse the tapered beam at 12 weeks of age (A) and at 20 weeks of age(B) and have a greater number of foot slips compared to WT (D and E), respectively. Similar performance deficits are seen in CMT1A rats at 17 weeks of age (C and D).
Nerve Conduction Deficits in CMT1A Mice and Rats
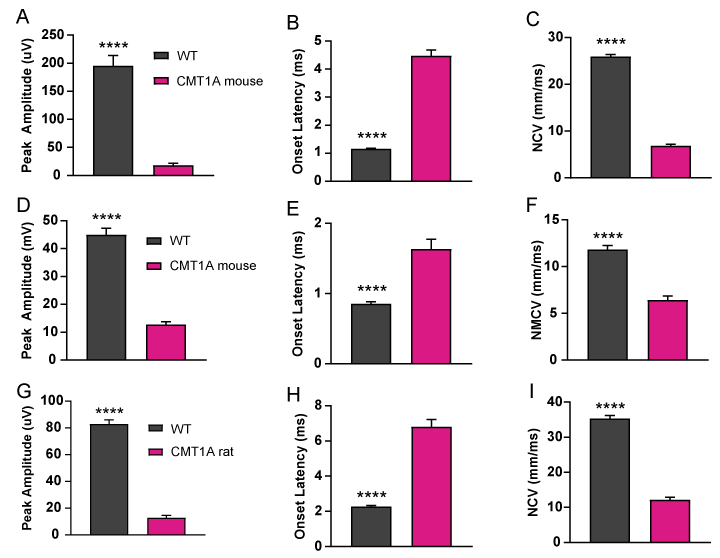
Compound action potential (A-C, mice 12 weeks of age; G-I, rats 17 weeks of age) and compound muscle action potential (D-F, 14 weeks of age) in WT and CMT1A animals. CAP responses were obtained from mixed nerve bundles in the tail, comprised of largely sensory axons. CMAP responses were obtained from the gastrocnemius muscle following sciatic motor nerve stimulation. In both CAP and CMAP responses, we see robust phenotypic deficits in CMT1A animals.
Myelination Defects in CMT1A Mice and Rats
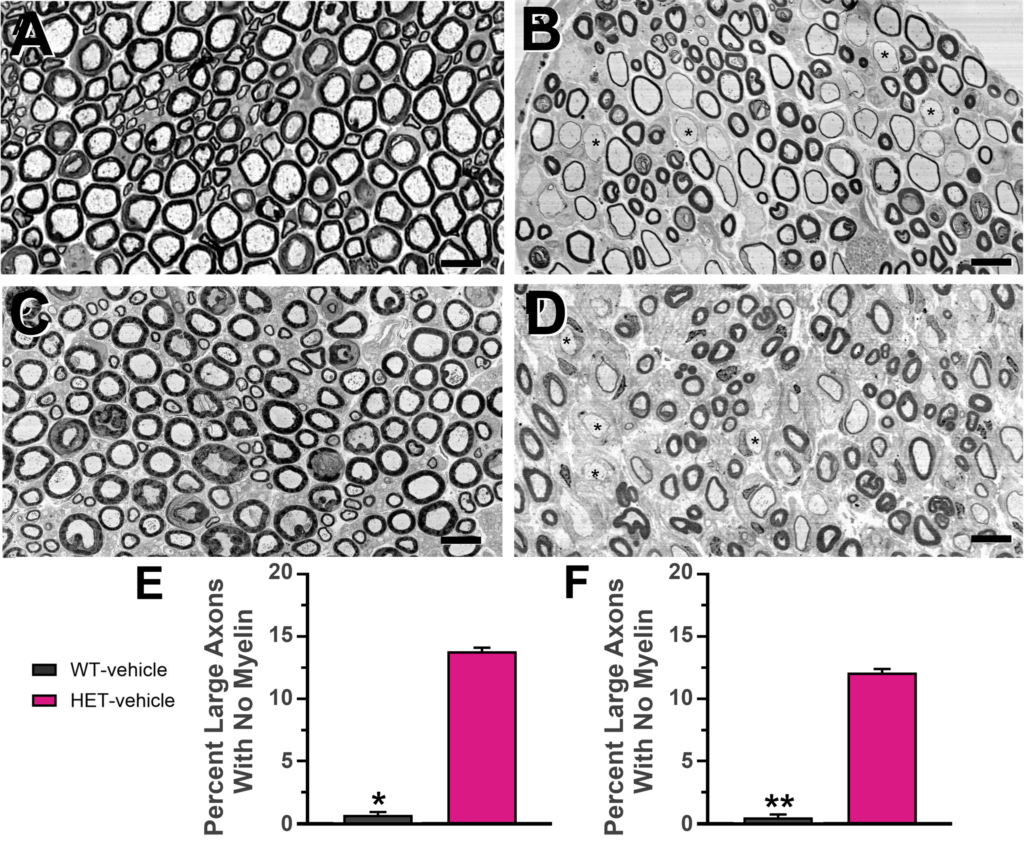
Electron microscopic analysis of femoral nerve motor branch segment from WT and CMT1A mice (A, B, and E, 21 weeks of age) and rats (C, D and F, 18 weeks of age). In WT animals (A, C) large motor axons (diameter > 3.5 mm) are myelinated. In CMT1A animals (B, D), axons have much thinner or no detectable myelin. Axons without myelin comprised 14% (E, F) of large axons. Scale bars 10 mm.
Acknowledgment: The C3 mouse model of CMT1A was obtained by the CMTA from Amsterdam UMC, courtesy of Prof. Frank Baas. The rat model of CMT1A was obtained by the CMTA from the Max Planck Institute-Göttingen, courtesy of Prof. Klaus Nave.
Electron Microscopic analysis was conducted by Dr. Graham Kidd at the Cleveland Clinic.