rTg4510 mice overexpress human tau containing the P301L mutation downstream of a tetracycline operon-responsive element (TRE). Expression is driven by a second transgene expressing the tetracycline-controlled transactivator (tTA) under control of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II α (CaMKII α) promoter. tTA constitutively induces tau expression via the TRE, but can be inactivated with doxycycline (DOX) administration. This model recapitulates tau pathology observed in AD with age-dependent and region-specific progression of neuronal loss resulting in cognitive impairment.
Behavioral and Cognitive Deficits in rTg4510 Mice
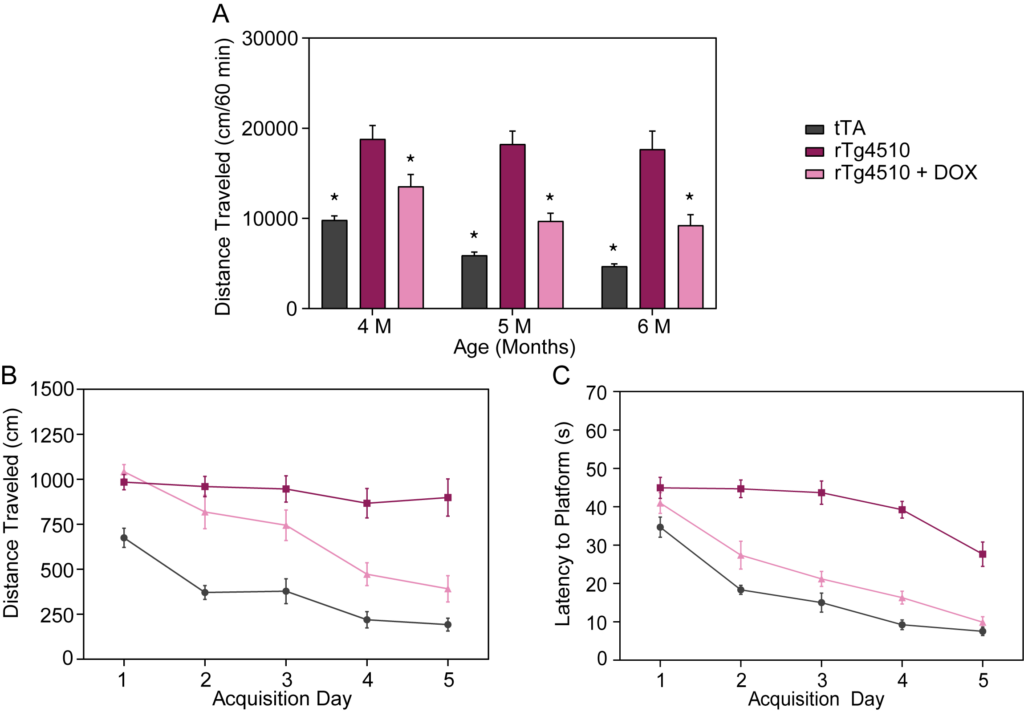
(A) Female rTg4510 mice at 4, 5, and 6 months of age show hyperactivity in the open field test that is reversed by DOX treatment. (B, C) rTg4510 exhibit cognitive deficits in the Morris water maze test at 6 months of age. Compared to tTA mice, rTg4510 take more time (B) and travel longer distances (C) to reach the hidden platform. Treatment with DOX (200ppm in chow) for 18 weeks attenuates these deficits.
LTP Deficits in rTg4510 Mice
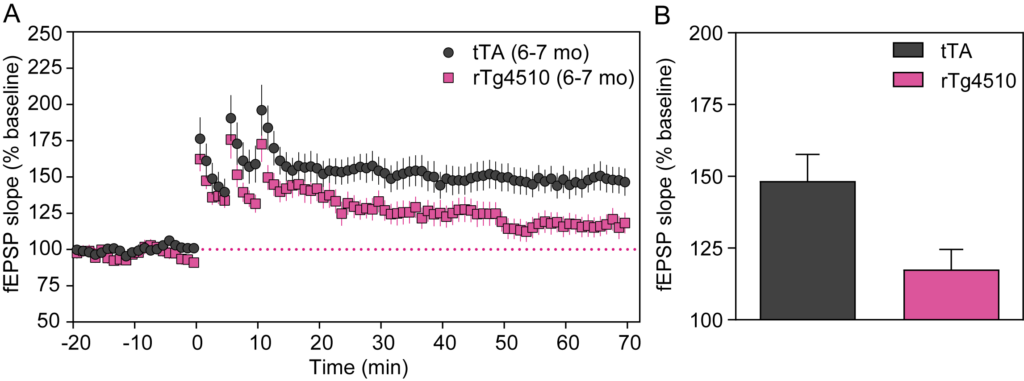
(A) rTg4510 mice show changes in EEG power spectra. The EEG recordings in parietal cortex show higher gamma power in tTA mice compared to rTg4510 mice. (B) A time-course of evoked responses (fEPSP slope normalized to the baseline) show LTP deficit in rTg4510 mice. (C) Summary of data taken from the last 5 minutes of recordings. A concurrent reduction in both presynaptic and postsynaptic function in rTg4510 hippocampal slices is consistent with overall neurodegeneration, with the observed LTP deficit reflecting a loss of synapses.
Pathological Changes in rTg4510 Mouse Brain

Pathological changes in frontal cortex were examined in female tTA (upper panel) and rTg4510 mice (lower panel) at 6 months of age. Left panel shows accumulation of pTau (green) as well as strong microglial activation. Middle panel shows C1q complement activation that is absent in the tTA. Right panel shows prominent reactive astrogliosis and microglial activation.
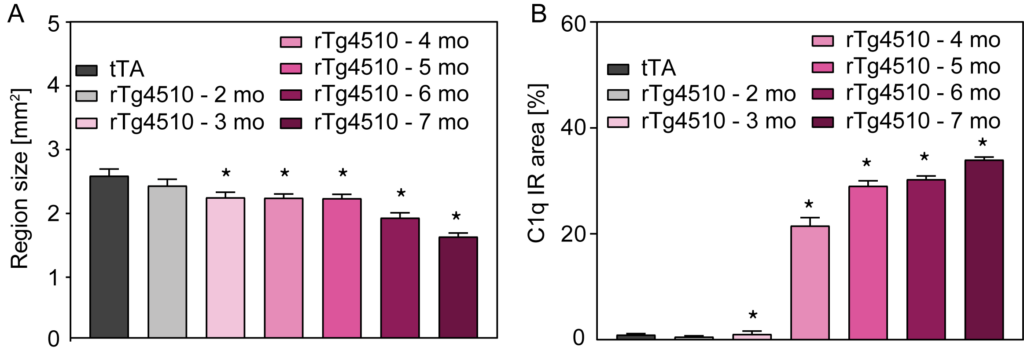
(A) Progression of atrophy shown as average region size per section with a significant progression between 5 and 6 months of age; (B) Complement activation by C1q immunoreactive area shows a drastic increase at 4 months of age, which further increases with age.
Phospho-Tau Accumulation in rTg4510 Mouse Brain
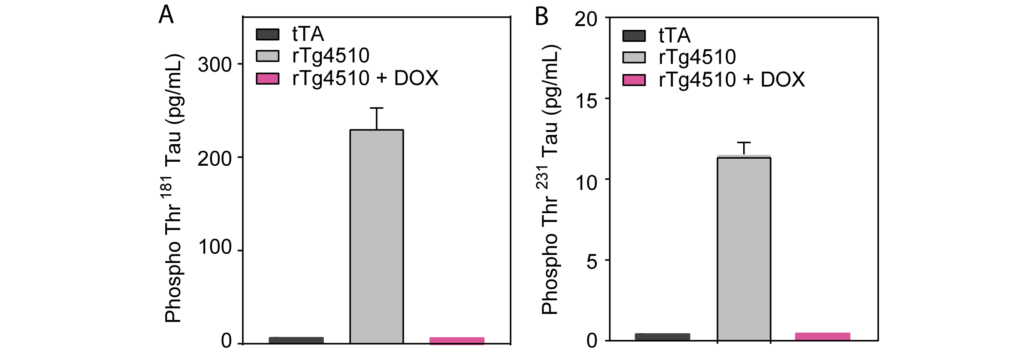
6-month-old female rTg4510 mice express higher phosphorylated Tau protein levels compared to tTa mice. Doxycycline treatment over 18 weeks significantly reduced phospho Thr181 Tau (A) and phospho Thr231 Tau (B) protein levels in rTg4510 mice.
rTg4510 Mice Exhibit Elevated Neuroinflammatory Markers
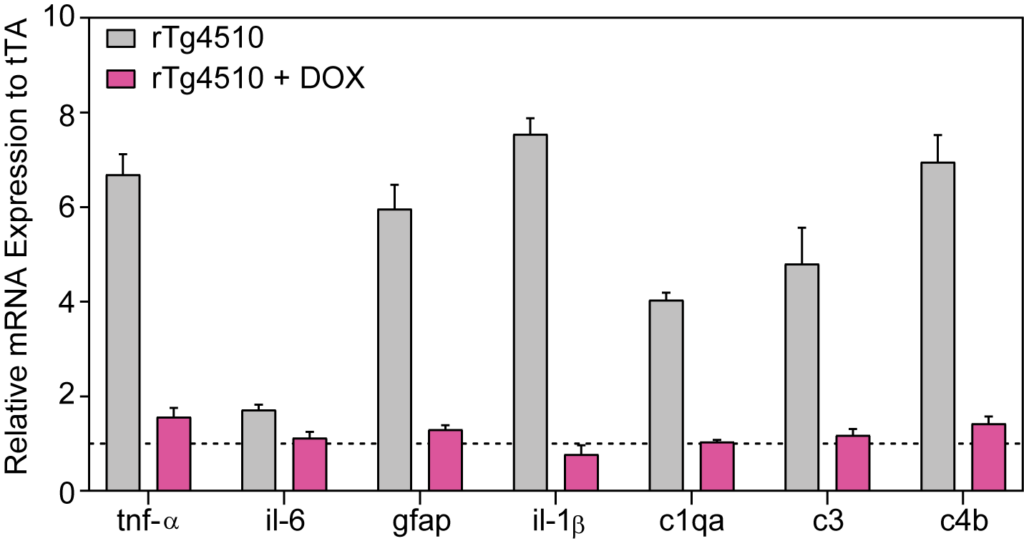
mRNA levels of neuroinflammatory markers are elevated in hippocampal tissues of rTg4510 mice at 5 months of age. Doxycycline treatment reduced all inflammatory markers.